
About Otorhinolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology is the medical discipline involving the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases, abnormalities, and other health problems affecting the ears, nose and throat, as well as the head and neck, mouth, sinuses, and voice box (larynx).
Specialists in the field are called otorhinolaryngologists or ENT specialists. Aside from medical management, they are also trained to perform surgeries that involve the above-mentioned body parts, including plastic or reconstructive surgeries.
Otorhinolaryngologists May Specialize In The Following Areas:
- Sleep medicine – Certain sleeping disorders such as sleep apnoea can be attributed to abnormalities in the nose (e.g., septum deviation) or obstruction in the throat and the airway passage. Thus, some cases can be covered by ENT specialists.
- Allergy – Otorhinolaryngologists are expected to learn about the pathology of allergies. They are also trained to properly assess and treat allergies using treatment options that can range from medication to immunotherapy. They are also responsible for the prevention and management of the condition.
- Head and neck – Otorhinolaryngologists trained in head and neck treatment and management are expected to have in-depth knowledge in oncology. They provide scientifically proven treatment and therapies as well as perform surgery to remove both benign and malignant tumours or to treat congenital deformities, and provide trauma care.
- Facial surgery – Surgery can be either reconstructive in nature, which aims to restore the appearance or function of the affected body part, or plastic, which enhances the look of the body part especially the nose and ears.
- Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology – These are otorhinolaryngologists who work with children, which ages range from 0 to 12 years old. More often than not, they deal with congenital defects, trauma, and infections affecting the ears and throat.
When To See An ENT Specialist?
ENT specialists or otorhinolaryngologists can treat the following conditions:
- Pain, especially if it does not go away despite taking medication (a perfect example is a pain in the ear. Sometimes, it becomes painful when a person is suffering from a common cold or flu. But if the symptoms of common cold and flu are gone but the pain remains after medication, it is possible the cause of ear pain is an infection).
- Infection affecting the structures of the ears, nose, and throat
- Malignant and benign tumours or polyps in the structures of the ears, nose, throat, head, and neck birth defects
- Diseases affecting the structure of the mouth and jaw, excluding the teeth and gums, which are best handled by dental professionals.
- Decreased function of the ears, nose, head, and neck (e.g., hearing loss)
- Obstructive sleep apnoea, a kind of sleeping disorder
- Allergies including allergic rhinitis and asthma
- Acid reflux (GERD)
- Symptoms such as a change in voice quality (e.g., hoarseness) or difficulty in swallowing
- Balance disorders
- Sinusitis and migraine
- Developmental delays among children
- A disease affecting the sinuses
- Cancers such as oral, salivary gland, and skin cancer affecting the head, neck, and nose
- Fractures and damage to the skin tissues
- Geriatric-related diseases
Otorhinolaryngologists may also be needed to perform:
- Microvascular surgery, which involves grafting skin and its blood vessels from one area (donor site) to another (recipient site). This requires extensive skills and steady hands since blood vessels are fragile and small.
- Maxillofacial surgery
- Parathyroidectomy (the partial removal of thyroid glands) and thyroidectomy (complete removal of thyroid glands), adenoidectomy (removal of adenoids), and tonsillectomy (removal of tonsils)
- Ear surgery
- Fitting of hearing aid
- Facelifts, septoplasty, and rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty, brow lift, and otoplasty
FAQs
- What Happens During A Typical Appointment with An ENT Specialist?
A visit to an ENT specialist or otolaryngologist is different from an average visit to your family physician, as the specialist may use instrumentation to allow better visualization of difficult areas.
Outlined below is what to expect from a general ENT visit, however, depending on the presenting symptoms of the patient, the consultation may vary, tailoring the history and the examination to the patient’s complaint and presenting symptoms.
Typically, a history is taken eliciting the symptoms of the patient’s complaints. It is also important that the past medical history and medication (always bring a current list with you) being used should be documented, as this may have relevance if one requires surgery at a later date. The history will become focused on the presenting complaint and its effect on the individual.
A thorough examination is usually undertaken, but some aspects of the examination outlined below may not be performed if not relevant to the complaint.
- EAR
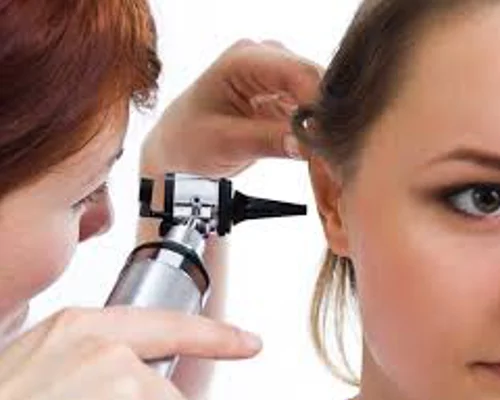
An otoscope is an instrument used to examine the ears and illuminate the eardrum so that the surgeon can identify normal landmarks and abnormalities. This instrument is made with an illuminating handheld light source with a small amount of magnification attached to it. It is not normally a painful experience and can usually be undertaken in all age groups.
In addition, the use of tuning forks as a gauge of hearing may sometimes be used as part of the consultation. However, sometimes it is required to undertake formal hearing tests to ascertain a more exact level of hearing. Occasionally, the eardrum and canal need to be viewed under magnification and a microscope can be used to provide this. The microscope allows the physician a more precise view of the ear structures and the use of suction if necessary, to remove wax or debris from an ear canal.
- NOSE
To look at the front of the nose, a simple tool called a nasal speculum together with illumination from a headlight is used to visualize the anatomy and possible abnormalities. In many cases, a flexible instrument called a fiberoptic scope as described below might be used to inspect the nose and throat more thoroughly.
- THROAT
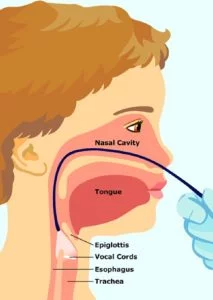
An external examination of the neck is not uncommon to feel for any glands or pathology. This is undertaken manually feeling the different areas of the neck in a methodical fashion. The oral cavity is thoroughly examined often with a tongue depressor and good illumination to visualize the tongue and tonsillar area. It is not uncommon to visualize the back of the nose and the vocal cords with a flexible nasolaryngoscope.
This is a fine fiberoptic cable with a small lens on one end and an eyepiece on the other that is inserted into the nose. The nasal passageway will be sprayed with an anesthetic prior to the insertion of the scope. During Insertion of the scope, it might feel a bit strange, however, it is essential to allow the surgeon a superb view of areas that are very difficult to examine otherwise. The whole procedure usually takes a few minutes, and it is often required as part of a thorough ENT examination.
The summary above is provided as a guide to the full ENT examination, which may be completely undertaken or tailored to an individual’s need.
The ENT specialist may perform a procedure called a laryngoscopy or nasal endoscopy with a thin flexible instrument that has a lighted magnifying tip which is passed through the nose. This additional procedure is essential to discover the cause of voice and breathing problems, ear or throat pain, difficulty swallowing, narrowing, blockages or even tumors or cancer.
- What Are Some Of The Disorders And Diseases That Ear, Nose, Throat Doctors Treat?
Treating nasal cavity and sinus issues is one of the primary skills of ENT doctors. We also treat diseases of the throat, larynx—more commonly known as the voice box—and the upper esophagus, including voice and swallowing disorders. These issues can affect speaking, singing, eating and the sense of smell. The head and neck also house functions associated with sight and the cosmetic appearance of the face so ENT’s are trained to treat infections, both noncancerous and cancerous tumors and facial trauma and deformities of the face, and we perform both cosmetic plastic and reconstructive surgery.
- How Common Are These Disorders/Diseases?
Very common. They are probably ranked among one of the top illnesses that people have to face. For instance, about 35 million people develop chronic sinusitis each year, making it one of the most common health complaints.

