About Hernia
A Hernia is a protrusion or a bulge around the abdominal area and usually occurs due to a weakness or a hole in the muscular wall that keeps the abdominal organs in place. This weakness or defect in the peritoneum allows tissues or organs to herniate or push through the muscular wall, which results to producing a bulge.
Hernias commonly occur in the abdominal area but can also occur in the groin and upper thigh areas. The bulge may not be visible in when a person lies down but it can be pushed back in, however, coughing
may make it reappear.
Types Of Hernia
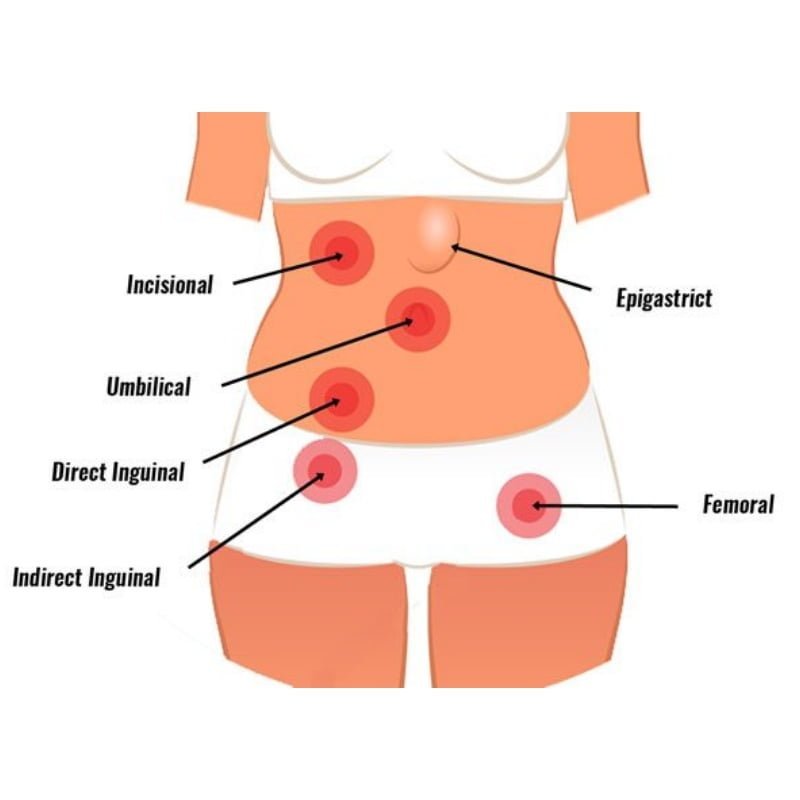
Hernias can commonly be found in the following areas:

Groin
A Femoral Hernia creates a bulge just below the groin and is more common in women whereas an Inguinal Hernia is common in is found in the groin area that may reach the scrotum.

Stomach
A Hiatal or Hiatus Hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach pushes out of the abdominal cavity and into the chest cavity through an opening in the diaphragm

Belly Button
An Umbilical Hernia occurs when the intestines protrude from the abdominal wall and appear near the belly button
Surgery Scar
An Incisional Hernia occurs in areas where a previous surgery scar leads to a weakness in the abdominal muscles at the surgical site.
Symptoms Of Hernia
Common hernia symptoms include:
- Tender bulge or lump that cannot be pushed back into the abdomen
- Discomfort and pain when standing, straining, or lifting heavy items
- Nausea & Vomiting
- Acid Reflux & Heartburn
- Difficulty in swallowing food
- Chest pain
Causes Of Hernia:
A Hernia happens due to a combination of strain and muscle weakness. Depending on the cause, a hernia may develop over a period of time or rather quickly. The primary reason for a Hernia is the increased pressure on a weak point in a muscle wall around your belly resulting in an organ or tissue to bulge through the weak area. The risk of hernia increases with age and occurs more commonly in men than in women. A hernia can also develop in children born with a weakness in their abdominal wall at birth.
Common Causes Include:
- Strain due to constipation while passing stool
- Physical exertion
- Strain during urination
- Chronic coughing
- Cystic fibrosis disorder
- Enlarged prostate
- Multiple pregnancies
- Being overweight Abdominal fluid
- Lifting heavy items
- Peritoneal dialysis
- Poor nutrition
- Smoking
- Undescended testicles
When To See A Doctor?
Most hernias are not immediately life-threatening, but they do require surgery to prevent dangerous complications as they don’t go away on their own. In some cases, the hernia may need immediate surgery. Early medical care and changes in lifestyle can minimize the symptoms of a hernia, however, the only way to effectively treat a hernia is to get surgery done. There are different types of surgeries for different types of hernia and a consultation with your surgeon is required in order to go ahead with the surgery which is right for your condition.
Factors That Increases The Risk Of Developing A Hernia:
The risk factor can be broken down by hernia type:
1. Incisional Hernia
Because an incisional hernia is the result of surgery, the clearest risk factor is a recent surgical procedure on the abdomen. People are most susceptible 3-6 months after the procedure, especially if:
• They are involved in strenuous activity
• Have gained additional weight
• Become pregnant these factors all put extra stress on tissue as it heals
2. Inguinal Hernia
Those with a higher risk of an inguinal hernia include:
• Older adults
• People with close relatives who have had inguinal hernias
• People who have had inguinal hernias previously
• Males
• Smokers, as chemicals in tobacco, weaken tissues, making a hernia more likely
• People with chronic constipation
• Premature birth and low birth weight
• Pregnancy
3. Umbilical Hernia
Umbilical hernias are most common in babies with low birth weight and premature babies.
In adults, the risk factors include:
• Being overweight
• Having multiple pregnancies
• Being female
4. Hiatal Hernia
The risk of hiatal hernia is higher in people who:
• Are aged 50 years or over
• Are obese
Treatment Options For Hernia:
For a hernia without symptoms, the usual course of action is to watch and wait, but this can be risky for certain types of hernia,
such as femoral hernias.
Within 2 years of a femoral hernia being diagnosed, 40 percent result in bowel strangulation. A complication where blood supply is cut off to an area of tissue, which requires an emergency procedure. An earlier routine operation is preferable to a more risky emergency procedure
Types Of Surgeries:
Although surgical options depend on individual circumstances, including the location of the hernia, there are two main types of surgical intervention for hernia:
• Open surgery
• Laparoscopic surgery (keyhole or minimally invasive surgery)
Open surgical repair closes the hernia using sutures, mesh, or both, and the surgical wound in the skin is closed with sutures, staples, or surgical glue.
Laparoscopic repair is used for repeat operations to avoid previous scars, and while usually more expensive, is less likely to cause
complications such as infection.
Benefits Of A Laparoscopic Surgery:
Surgical repair of a hernia guided by a laparoscope allows for the use of smaller incisions, enabling faster recovery from the operation.
Surgical instruments are inserted through another small incision. The hernia is repaired in the same way as in open surgery, but it is guided by a small camera and a light introduced through a tube. The abdomen is inflated with gas to help the surgeon see better and give them space to work; the whole operation is performed under general anaesthesia
FAQs
- Can a bulge in my groin or abdomen area be harmless?
A bulge in the groin area can indicate different kinds of problems. We advise a consultation with our expert hernia doctors to diagnose the problem.
- Can Hernia be naturally treated?
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
- Should I get Laparoscopic or Open Surgery for Hernia?
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
- How much time will the surgery take?
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
- Is it possible for the hernia to reappear?
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.
- When can I resume daily activities after the surgery?
Your content goes here. Edit or remove this text inline or in the module Content settings. You can also style every aspect of this content in the module Design settings and even apply custom CSS to this text in the module Advanced settings.

